Authors:
(1) Hamid Reza Saeidnia, Department of Information Science and Knowledge Studies, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Islamic Republic of Iran;
(2) Elaheh Hosseini, Department of Information Science and Knowledge Studies, Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences, Alzahra University, Tehran, Islamic Republic of Iran;
(3) Shadi Abdoli, Department of Information Science, Université de Montreal, Montreal, Canada
(4) Marcel Ausloos, School of Business, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK and Bucharest University of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Romania.
Table of Links
RQ 4: Future of Scientometrics, Webometrics, and Bibliometrics with AI
RQ 5: Ethical Considerations of Scientometrics, Webometrics, and Bibliometrics with AI
Conclusion, Limitations, and References
RQ 3: AI and bibliometrics
In bibliometrics, AI can provide several specific benefits including Automated Data Collection, Citation Analysis, Author Disambiguation, Co-authorship Analysis, Research Impact Analysis, Text Mining, and Recommender Systems (see Figure 4) as analyzed in [28-30, 47-53].
These 6 studies demonstrate the potential benefits and strategies for utilizing AI capabilities in bibliometrics. They highlight how AI can improve the quality, accessibility, and data collection processes in bibliometrics analyses (Table 3), among the main outcome points.
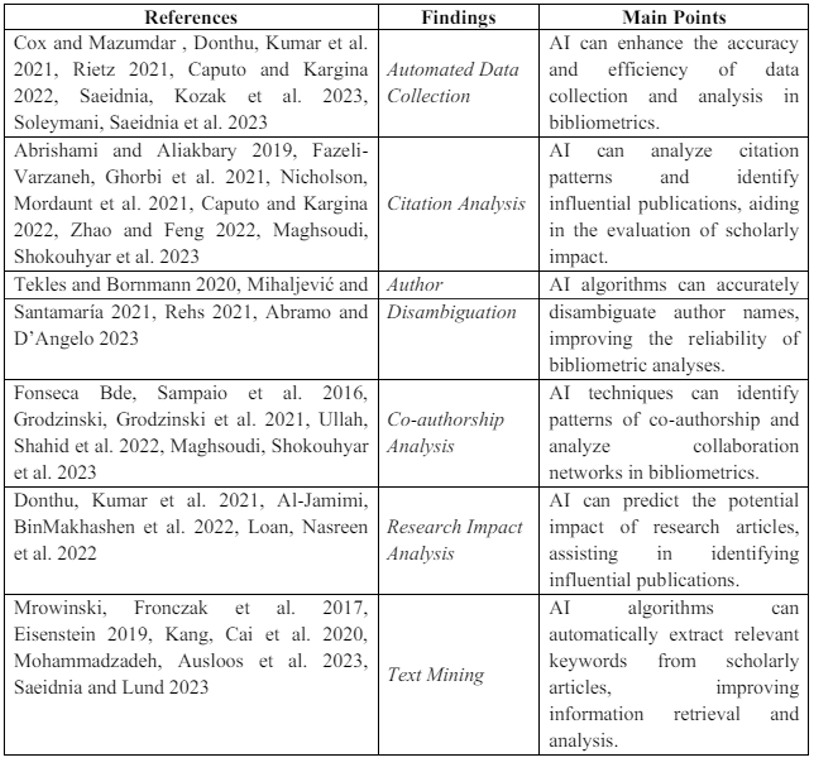
It has been shown that AI algorithms can automatically collect bibliographic data from various sources, such as online databases, academic libraries, and digital repositories [21, 49]. This saves time and effort for researchers involved in data collection, allowing them to focus on other aspects of bibliometric analysis.
Thought-provokingly, AI can analyze citation networks to identify influential papers, authors, and journals [28, 31], - as already mentioned in the section “AI and Scientometrics”. By examining citation patterns and relationships, AI algorithms can help researchers understand the impact and visibility of research outputs, as well as identify key research trends and collaborations.
Interestingly, AI techniques can be employed to disambiguate authors with similar names, a common issue in bibliometrics [47, 53]. By analyzing author affiliations, publication history, and co-authorship networks, in order to ensure the accuracy of bibliometric analyses, AI algorithms can effectively identify authors with similar names and distinguish them from one another.
As also already mentioned in the section “AI and Scientometrics”, through AI one can analyze co-authorship networks to identify collaborations and research networks [28, 30]. By examining co-authorship patterns and relationships, AI algorithms can help researchers understand the dynamics and structure of collaborations, as well as identify influential researchers and research teams. This can also be an advantage at funding time.
Easily, AI can analyze bibliometric indicators, such as citation counts and h-index, to assess the impact and visibility of individual researchers, research groups, and institutions [21, 48, 52]. In so doing, AI algorithms can provide insights into research productivity, citation patterns, and research impact over time, assisting researchers and institutions in assessing research fame or performance.
Last but not least, AI techniques, including natural language processing, can be utilized to analyze the textual content of research publications [50, 51]. In this manner, keywords, topics, and sentiments can be extracted from the literature, - also mentioning plagiarism control [54, 55], thereby facilitating comprehensive analysis and understanding of research findings [56].
This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.

